MOST COMMON REFRACTIVE ERRORS
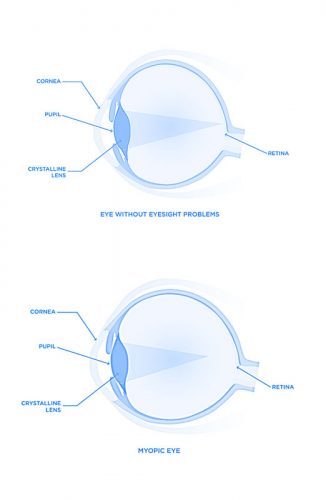
MYOPIA /Nearsightedness/ shortsightedness
it is widespread vision defect that characterized by difficulties to see far distant subjects; it may appear blurry. Today, myopia affects a growing number of people worldwide among younger people. Why it happens? Lack of outdoor activities and intensive screen use may accentuate it. This eyesight problem is most often caused by an eye that’s too long, where the distance between the cornea and the retina is too great. It also can be caused by the cornea and/or lens being too curved for the length of the eyeball. In some cases, myopia is due to a combination of these factors. Someone who’s myopic has difficulty seeing things far away because the image is formed in front of the retina. However, s/he sees well close-up. The more a person is myopic, the closer they need to get to an object to see it clearly.
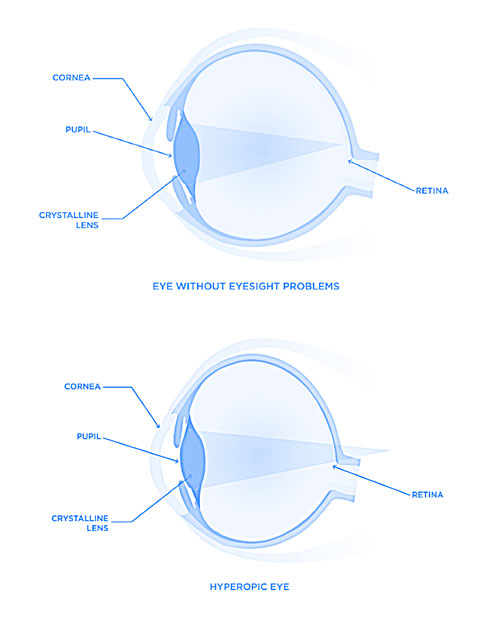
Hyperopia / Farsightedness
It is a common vision condition in which you can see distant objects clearly, but objects nearby may be blurry or requires a constant effort to see them, so, this can provoke headache.
In the case of hyperopia, the eyeball is too short meaning the distance between the cornea and the retina is insufficient. Consequently, the image of an object forms behind the retina. It may also be caused by an abnormal shape of the cornea or lens. A person with low hyperopia therefore can only see by constantly adjusting and accommodating their view.
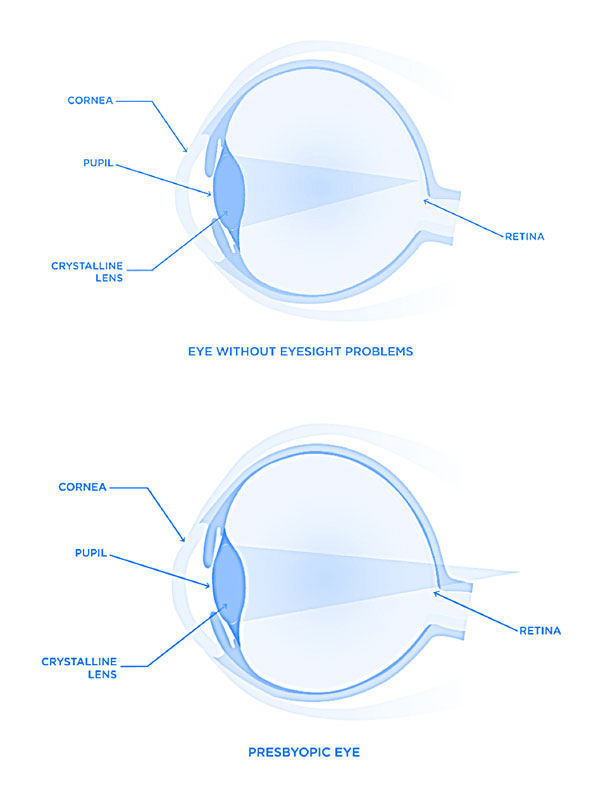
Presbyopia
=Presbyopia is not a visual defect but a natural evolution of our vision. No one is born with presbyopia but, we all develop it. It affects both women and men from the early 40’s onwards. It occurs when the eye is not able to focus clearly on close objects.
From 40 onwards, the lens loses some of its elasticity and its ability to accommodate. It is no longer able to ensure adjusting focus to see things close-up. Symptoms include difficulty reading small print, having to hold reading material farther away, headaches, and eyestrain.
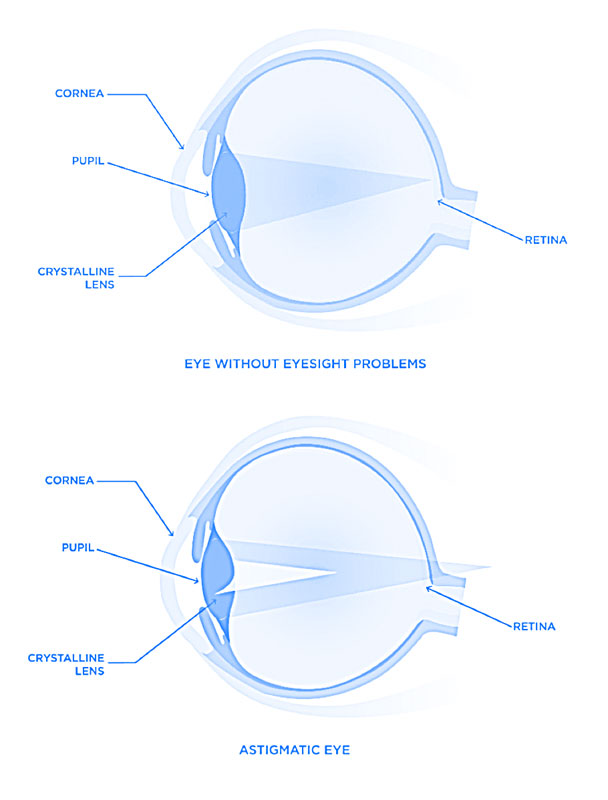
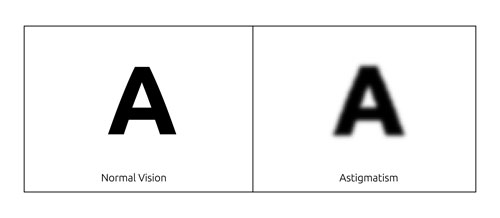
Astigmatism
Someone who is astigmatic has imprecise near and far vision. In particular, peripheral vision images can sometimes appear deformed. Astigmatism may be combined with other eyesight problems such as hyperopia, myopia.
COMMON SYMPTOMS OF ASTIGMATISM
• Headaches
• Eyestrain
• Distortion and blurred vision at all distances
• Difficulty in driving at night
• Squinting
Astigmatism is mainly caused by an irregular curvature of the cornea. As a result, the image is not formed properly on the retina, but distorted according to the curvature of the cornea.
VISION SOLUTIONS
LENS vision TYPE
Single Vision Lens: The wearer will have only one viewing area throughout the entire lens and help with one visual need.
The correctional area can be for far distance like driving etc., mid distance like computer work etc., reading or correct condition of Astigmatism. We use Freeform Lens Technology process for all our single vision processable Prescription range for maximum accuracy.
Bifocal Lenses: The lens is divided into two segments which offers usually distance viewing on the top and near vision on the smaller lower segment.
You can see visible lines depicting the division of sight distance. Generally, you look up and through the distance portion of the lens when focusing on points far away, and you look down and through the reading segment of the lens when focusing on near objects up to about armlength away.
Progressive Lenses: With progressive or multifocal lenses, you can look up to see in the distance, look ahead to view your computer in the intermediate zone, and drop your gaze downward to read and do fine work comfortably closeup.
Progressive or multifocal lenses Offers the similar functionality of a bifocal lens but allows smoother transition from far distance through intermediate to near; No visible line separates the different prescription looks cosmetically like single vision. We use High-end Freeform lenses Technology as our standard for ALL progressive prescriptions. This unique three-step process for superior back side digital lenses which integrates the results of real-wearer testing at each stage of the lens design.



